ABOUT THE SERVICE
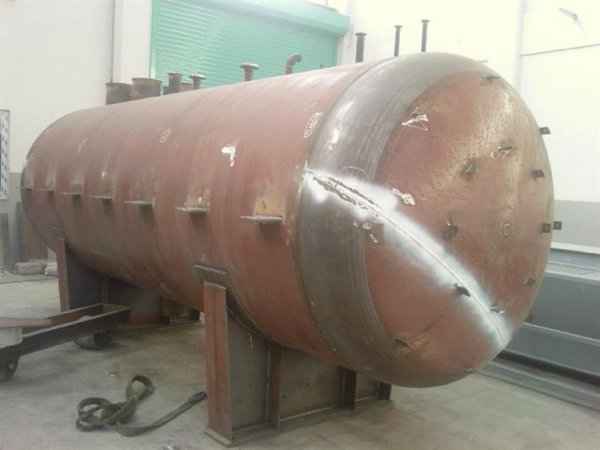
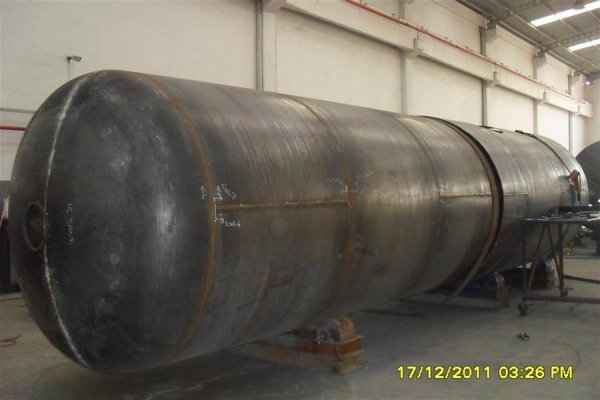
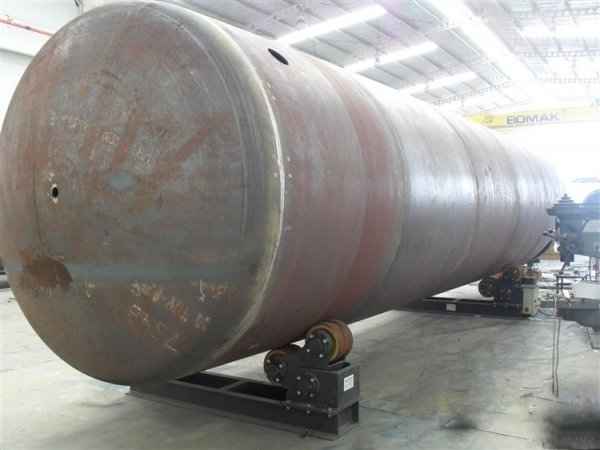
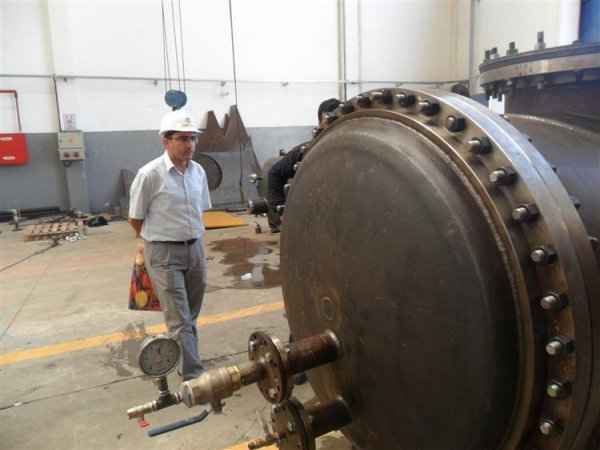
A pressure tank is designed to hold gases or liquids at pressures significantly different from the ambient pressure. Although pressure tanks are highly dangerous, fatal accidents have occurred throughout their development and operation history. Therefore, the design, manufacture, and operation of pressure tanks are regulated by engineering authorities supported by regulations.
The design of a pressure tank includes parameters such as maximum safe operating pressure and temperature, safety factor, corrosion allowance, and minimum design temperature (for fracture). Pressure tanks are tested through non-destructive inspection methods such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and pressure tests. Hydrostatic tests use water, while pneumatic tests use air or another gas. Hydrostatic testing is preferred as it is safer for pressure tanks because it releases less energy in the event of a leak.
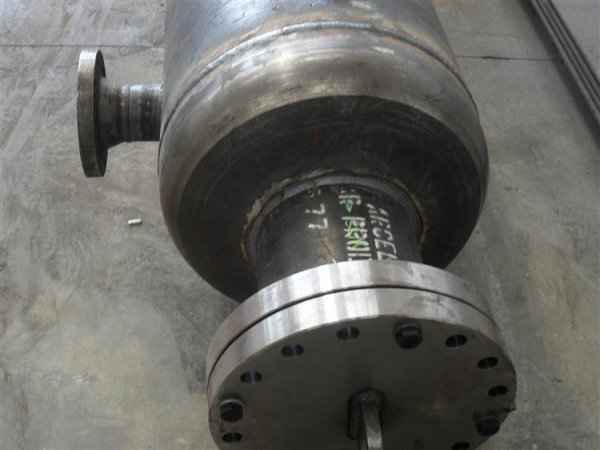
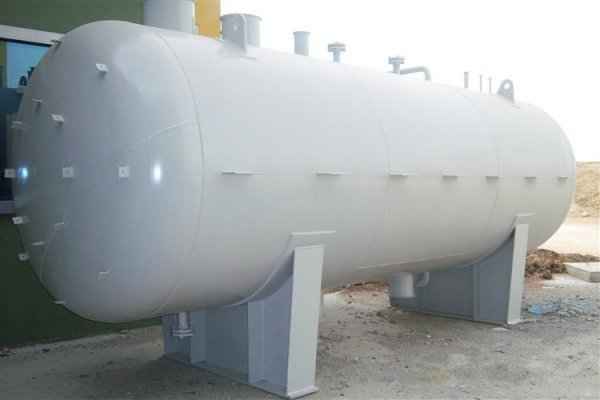
Pressure Tank Features
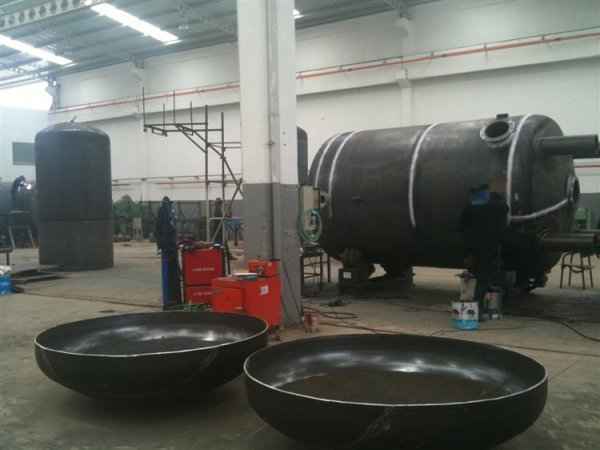
Pressure Tank Shapes
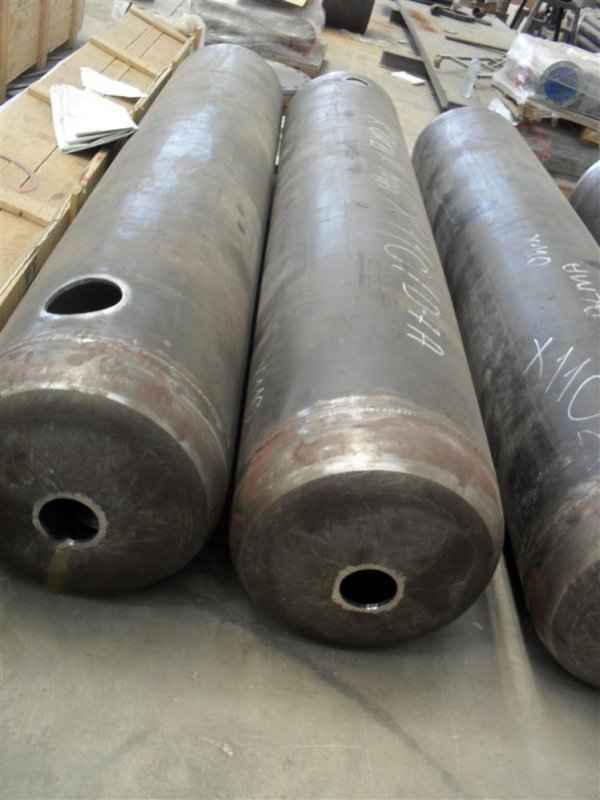
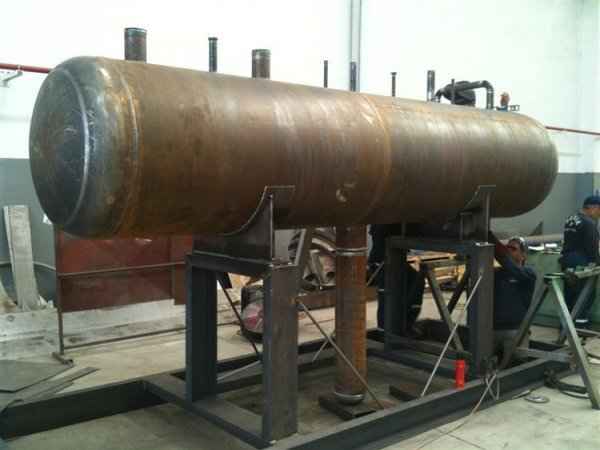
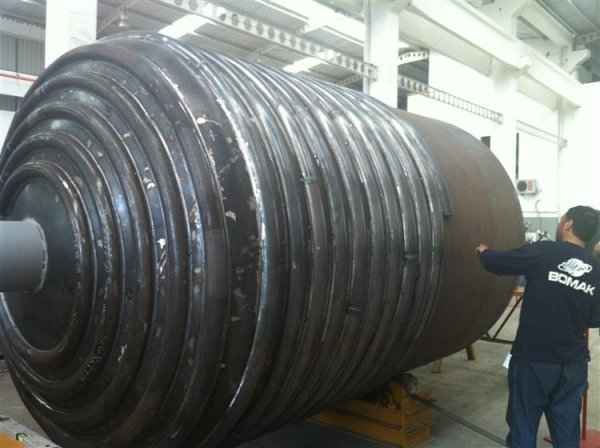
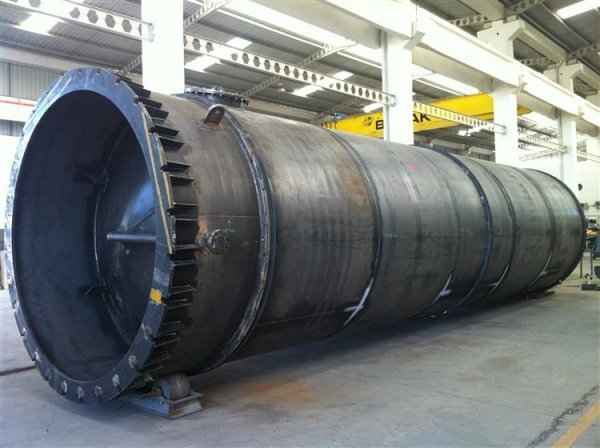
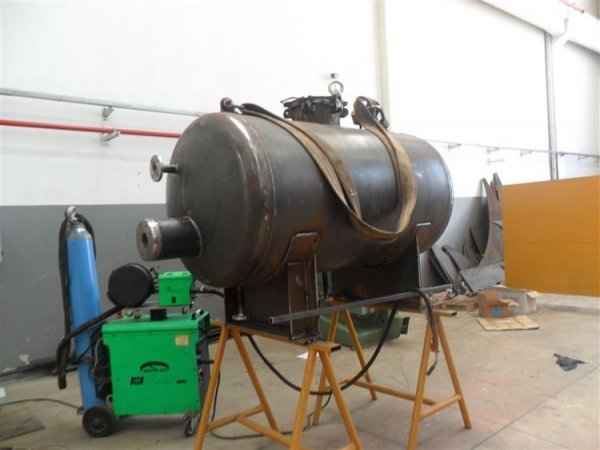
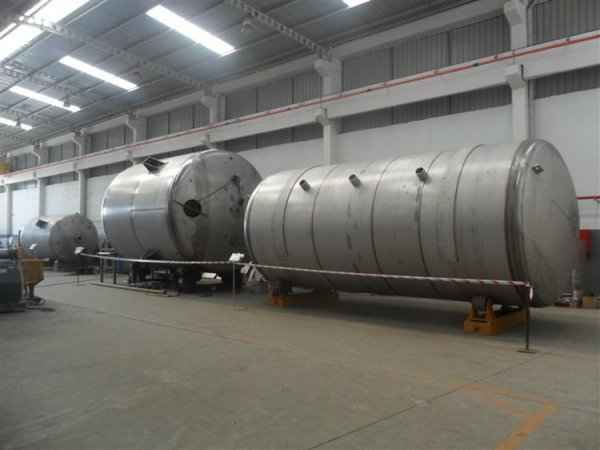
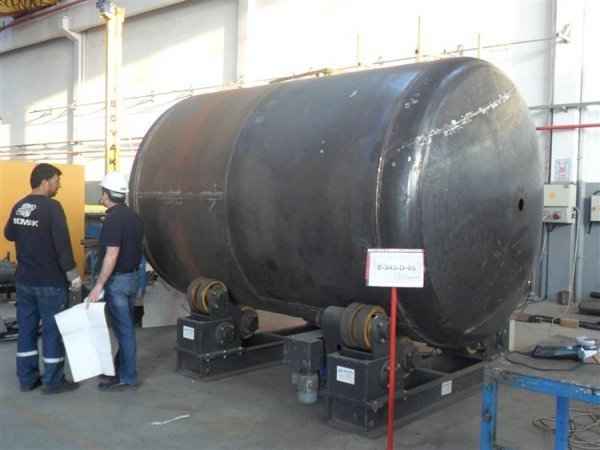
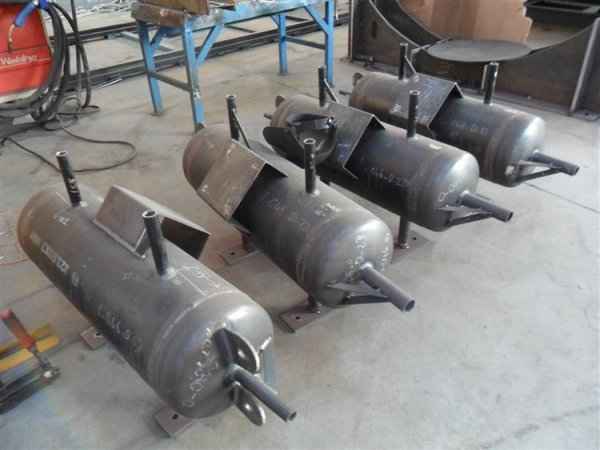
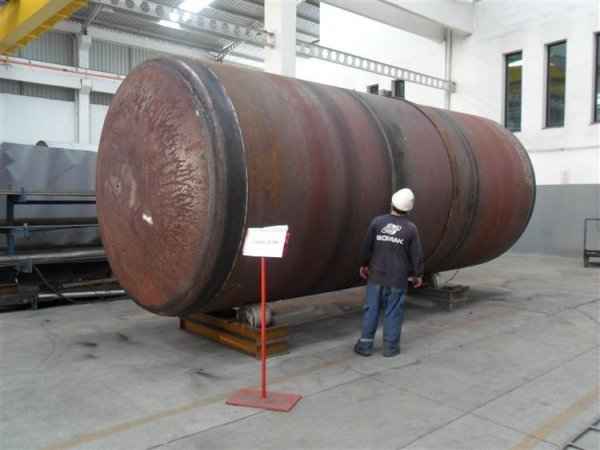
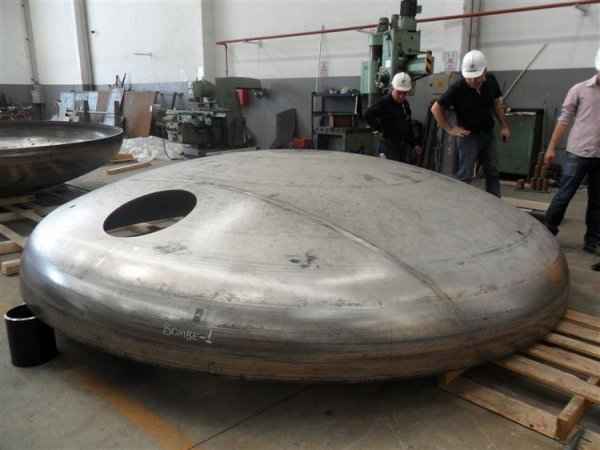
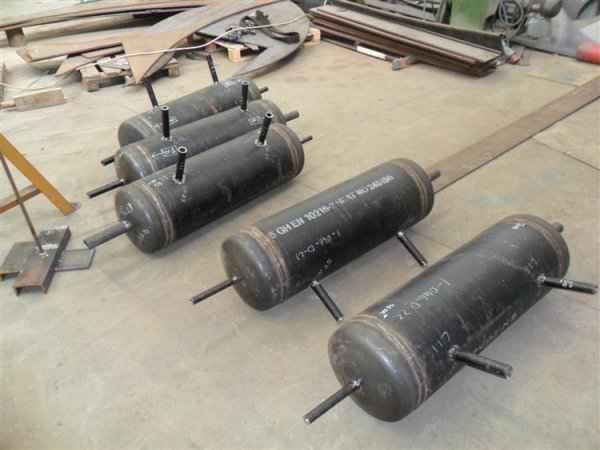
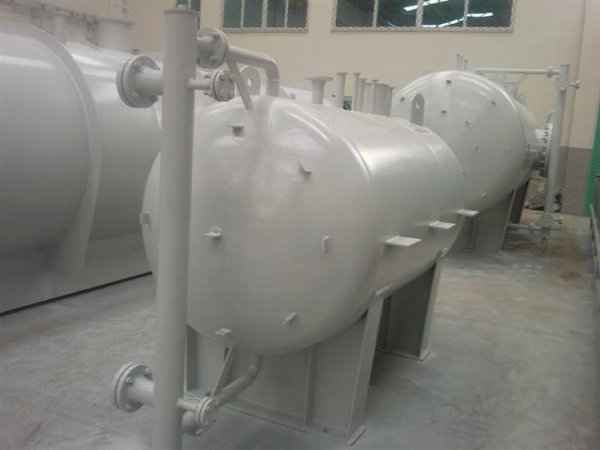
Pressure tanks can theoretically take almost any shape, but they are typically constructed in shapes consisting of spheres, cylinders, and cones. They commonly have a cylindrical design with end caps called heads. Head shapes are often hemispherical or convex (torispherical), while more complex shapes are not suitable for safe operation.
Construction Materials
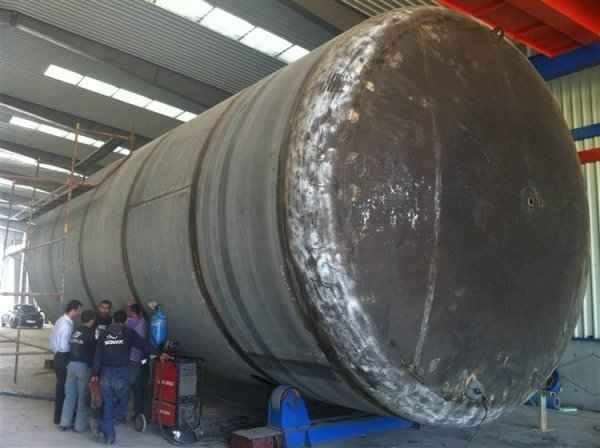
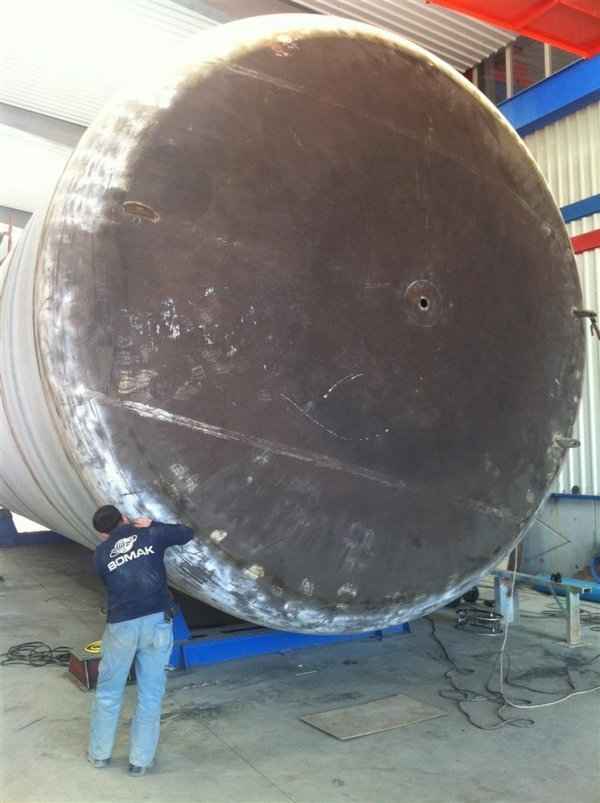
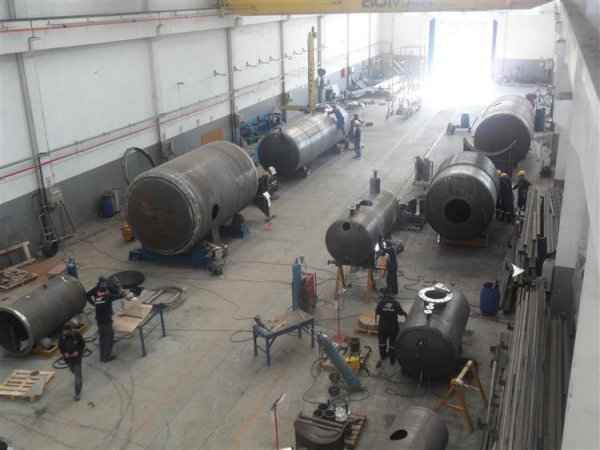
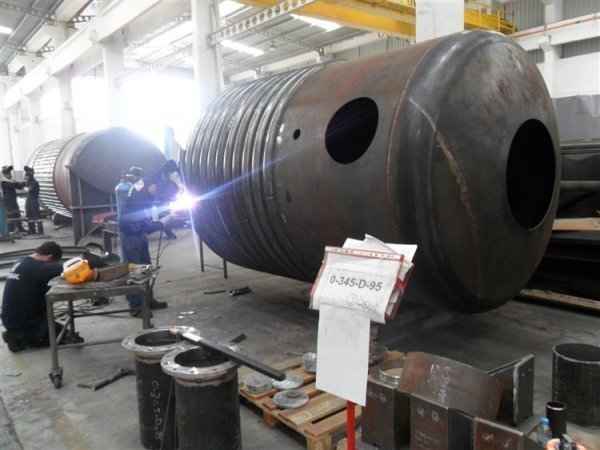
Steel is used for manufacturing pressure tanks with special methods. To produce a cylindrical or spherical pressure tank, rolled and forged parts must be welded together. Without special precautions during this process, some mechanical properties of the steel obtained by rolling or forging can be adversely affected by welding. In addition to mechanical strength, steel with high impact resistance is used for pressure tank materials, especially at low temperatures. In applications where carbon steel is prone to corrosion, special corrosion-resistant materials should be used.
Applications
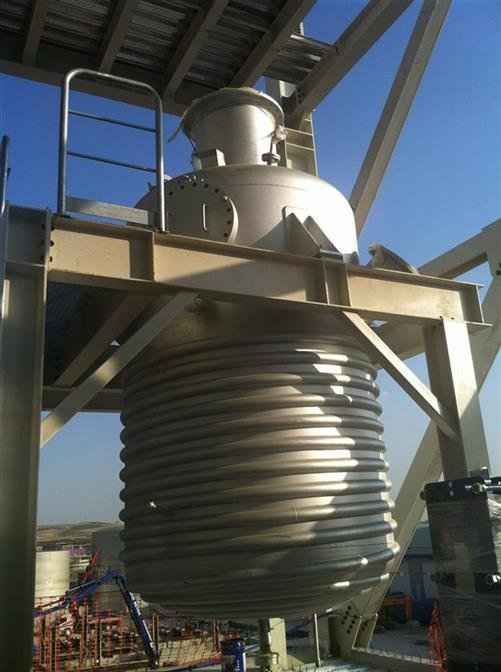
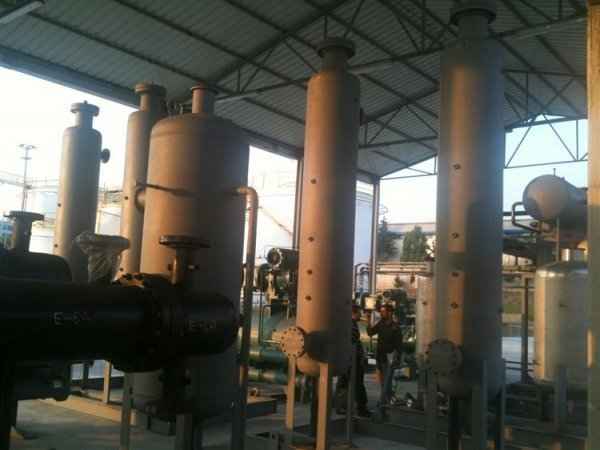
Pressure tanks are used in various applications both in industry and private sectors. They are found in industrial applications as pressure air receivers and hot water storage tanks. Pressure tanks are particularly popular in pressure chambers, distillation columns, pressure reactors, autoclaves, mining operations, oil refineries, petrochemical plants, nuclear reactor vessels, railway vehicle air brake reservoirs, road vehicle air brake reservoirs, and many other fields.